
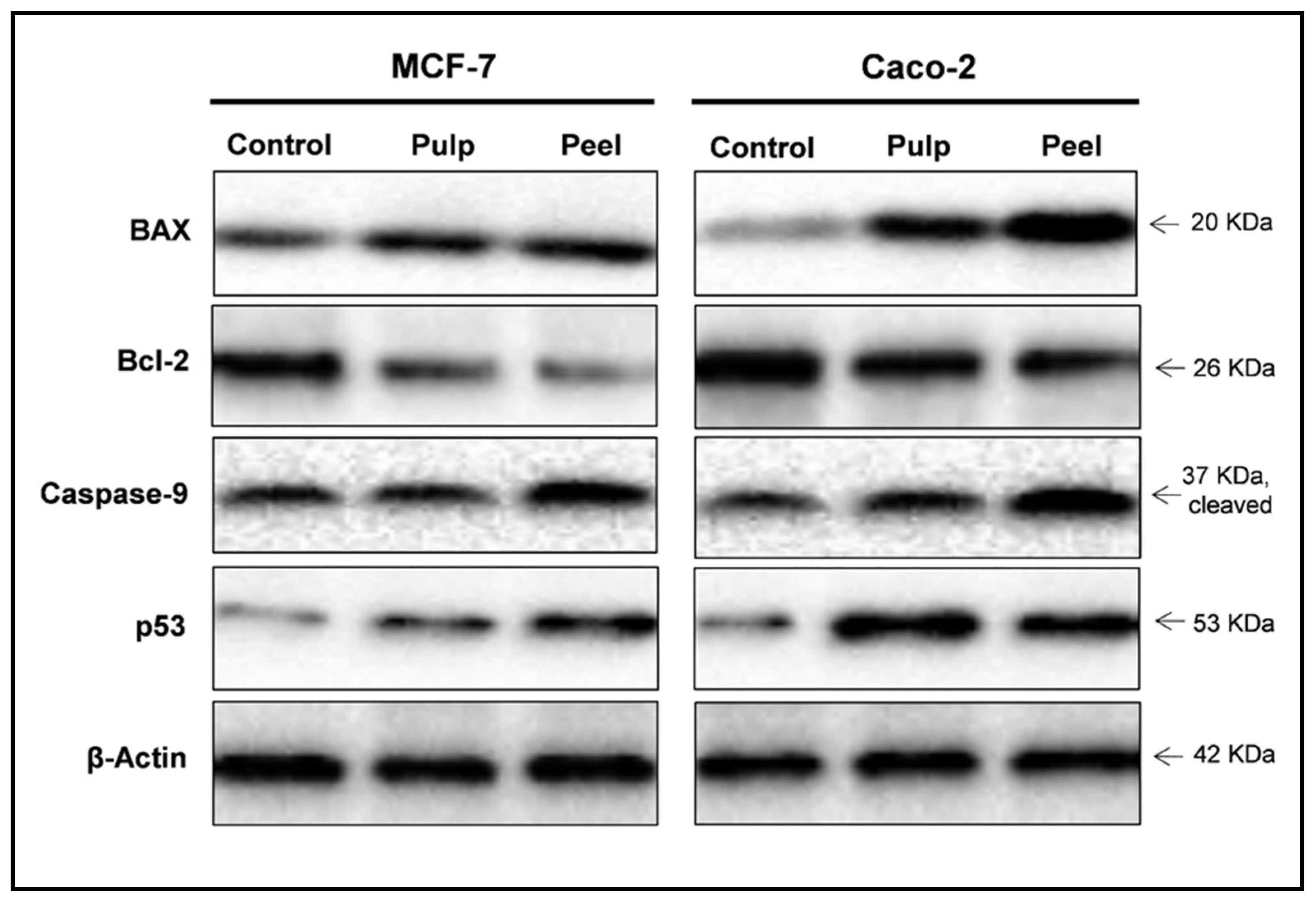
– Comparison of Key Differences Key TermsĪntibody, DNA, Electrophoresis, Northern Blotting, RNA, Proteins, Southern Blotting, Western Blotting What is the Difference Between Southern Northern and Western Blotting What are the Similarities Between Southern Northern and Western Blottingĥ. During blotting, the macromolecules are transferred onto a membrane from the gel and made to bind with a specific nucleic acid or antibody that aid in the detection. Southern, Northern, and Western are three blotting techniques used to detect a specific DNA, RNA or protein molecule in a sample.
Again, poor review quality has led to questionable data. The people who reviewed the previous paper allowed them to claim tissue expression by RT-PCR without protein, though they claimed to have had an antibody. Personally, I think the RT-PCR was too sensitive, as supported by the gene array data, and that the lack of qPCR with this lab, has led to the false assumption of wide spread multiple tissue expression. However, gene array analysis has shown very low, but wide-spread positive data for multiple tissues that do not show up by Northern, in situ, or our western, hence my original post. It is the previous pesky RT-PCR (non-quantitative mind you) that does not correlate. What we do know is that Northern blot data correlates with our Westerns (except for one tissue testes). As for correlating in situ with our Ab work, that is a great idea, and our western data supports the in situ work ( though the latter has been limited in scope). Others have been trying to knock out the gene, but it is embryonic lethal (or so I hear). Unfortunately, the null mouse does not exist. Our results clearly delineate the technical boundaries of current approaches for quantitative analysis of protein expression and reveal that simple deduction from mRNA transcript analysis is insufficient. Another interesting observation is that codon bias is not a predictor of either protein or mRNA levels. Conversely, invariant steady-state levels of certain proteins were observed with respective mRNA transcript levels that varied by as much as 30-fold. Indeed, for some genes, while the mRNA levels were of the same value the protein levels varied by more than 20-fold. We found that the correlation between mRNA and protein levels was insufficient to predict protein expression levels from quantitative mRNA data.
#Immunoblotting vs western blot serial
Corresponding mRNA levels were calculated from serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE) frequency tables (V. Protein spots were quantified by metabolic labeling and scintillation counting. Over 150 protein spots were excised and identified by capillary liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). The proteins contained in total yeast cell lysate were separated by high-resolution two-dimensional (2D) gel electrophoresis. We have determined the relationship between mRNA and protein expression levels for selected genes expressed in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae growing at mid-log phase.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
